Introduction
The repository, CannabinoidDB provides an overview of 5,652 CB1 molecules and 4,875 CB2 molecules. Further the molecules are classified into agonists, antagonists, inverse agonists and partial agonists. The interface is straightforward, easy-to-use and intuitive, allowing users to browse and search the database with ease.
CannabinoidDB has a simple and user-friendly interface for querying and browsing molecules. Visualizations of all the molecules in the receptor’s binding site are provided to understand relevant interactions. CannabinoidDB allows the user to interactively browse through the pages to access corresponding molecules and subsequently obtain details of the molecules along with their interaction details.
The following documentation provides users the information on browsing and navigating through the CannabinoidDB website easily and get the information they need, quickly.
About CannabinoidDB
Cannabinoid receptors 1 (CB1) and Cannabinoid receptors 2 (CB2) are the two types of receptors that are part of the endocannabinoid system. CB1 receptors are primarily found in the central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are present in the peripheral nervous system, immune system etc. The activation of cannabinoid receptors can have diverse effects like pain modulation, neuroprotection, immune regulation, appetite, metabolism as well as mood regulation.
Over the years, many cannabinoid databases have been developed. However, currently there is no online resource grouping all the known cannabinoid molecules at one place. Therefore, we developed CannabinoidDB that is a comprehensive database containing information about various endocannabinoids, phytocannabinoids as well as other synthetic cannabinoids that bind to these receptors.
Users can search for specific cannabinoid-receptor targeting molecules and view their chemical structures, physicochemical and ADMET properties along with their interactions with the CB1 and CB2 proteins. The data analysis module presented in the database includes descriptor calculation and scaffold analysis using powerful tools that can be used to analyze molecules in different ways.
You can find more information on CannabinoidDB by clicking on Read More button of the About Section of the Homepage.
Search and Browse
Basic Search
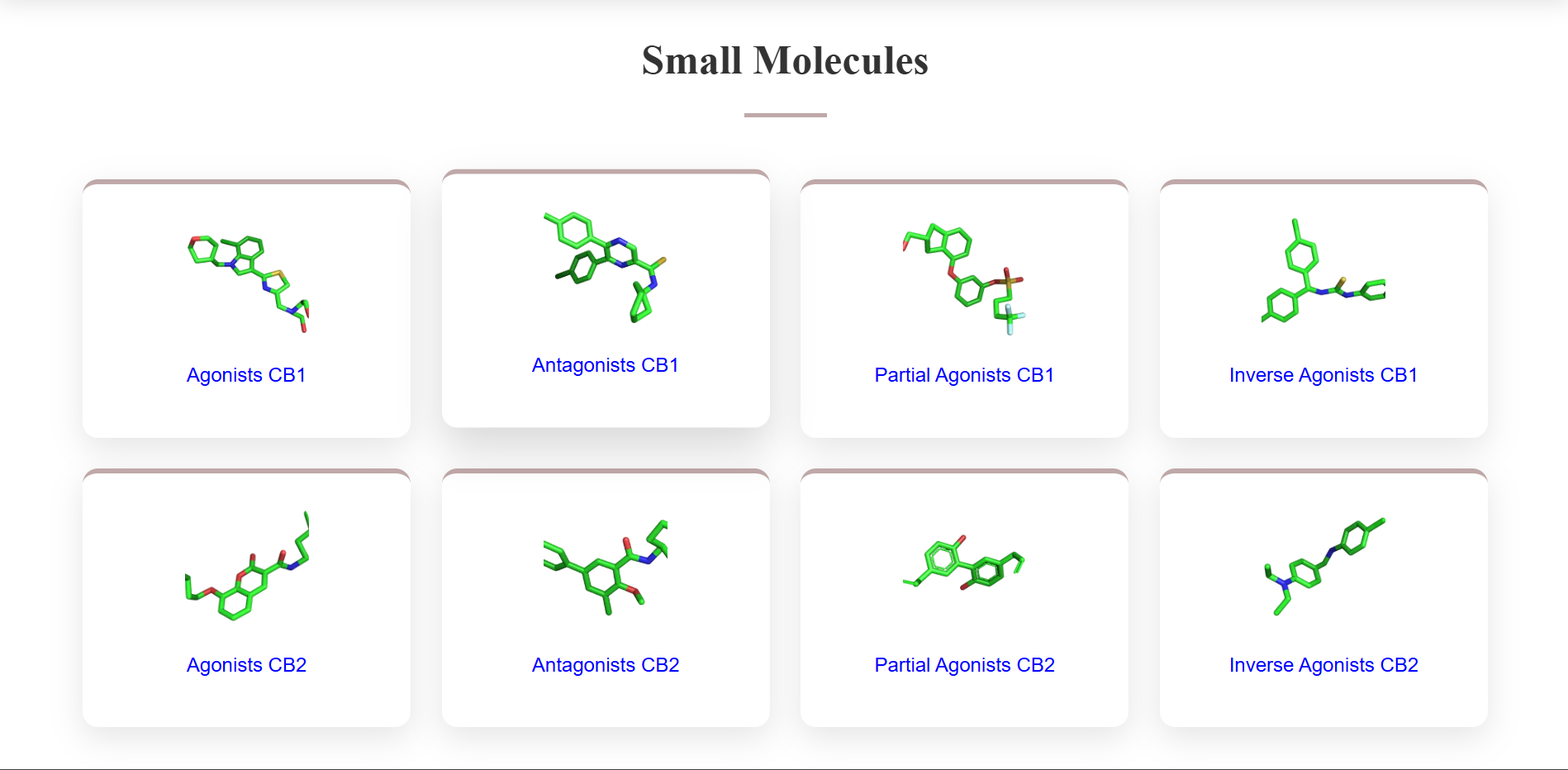
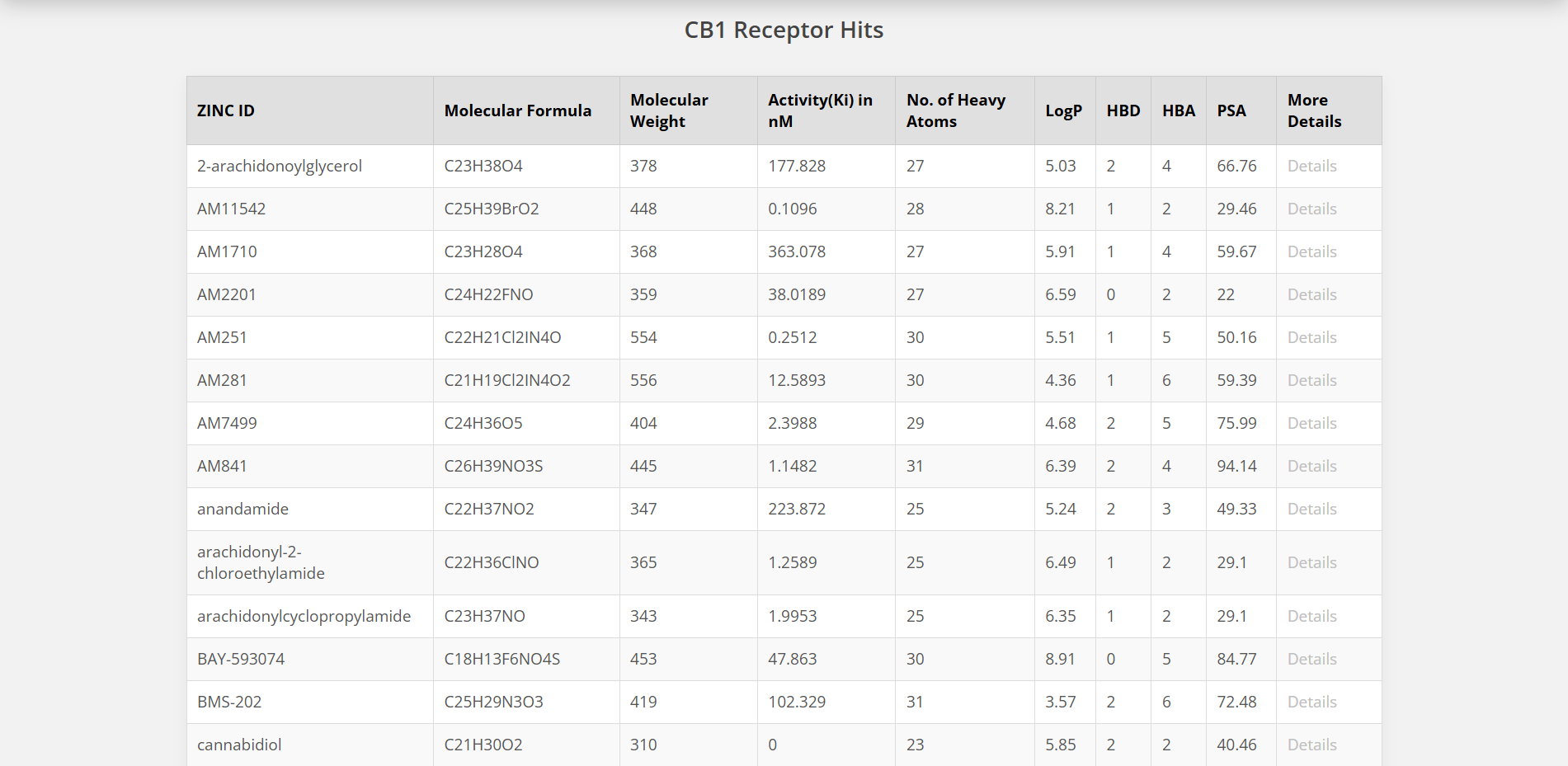
In the Small Molecules section of the Homepage, click on the type of small molecules you want to browse for, be it - Agonists of CB1, Antagonists of CB1, Agonists of CB2, Antagonists of CB2, Partial Agonists of CB1, Partial Agonists of CB2, Inverse Agonists of CB1 and Inverse Agonists of CB2.
After going into the respective database of your chosen molecules, use the SEARCH bar above to search for any specific ZINC IDs/ SMILES/Molecular Weight.
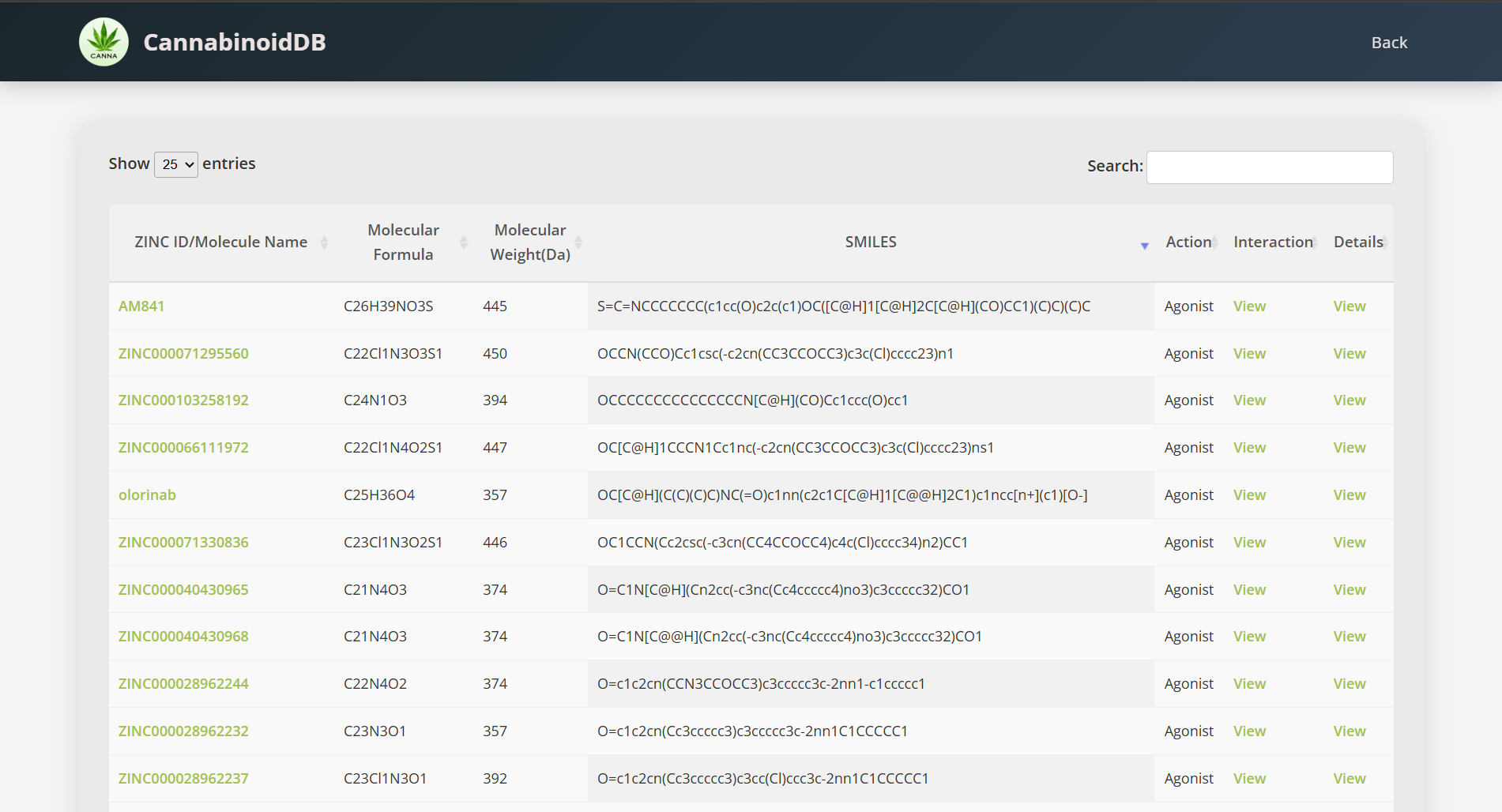
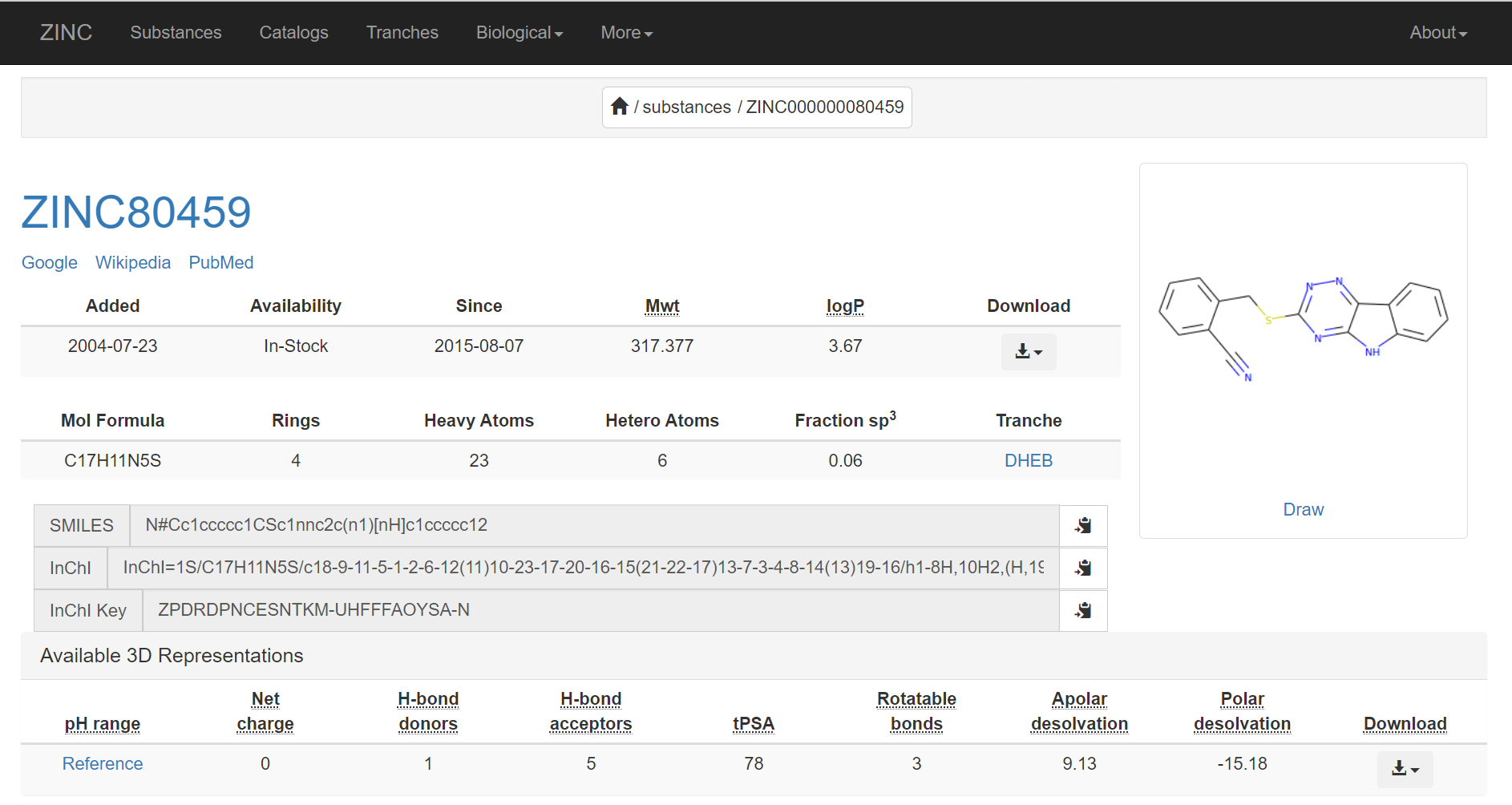
To have more information about the molecule from the ZINC database, click on the clickable ZINC ID link.
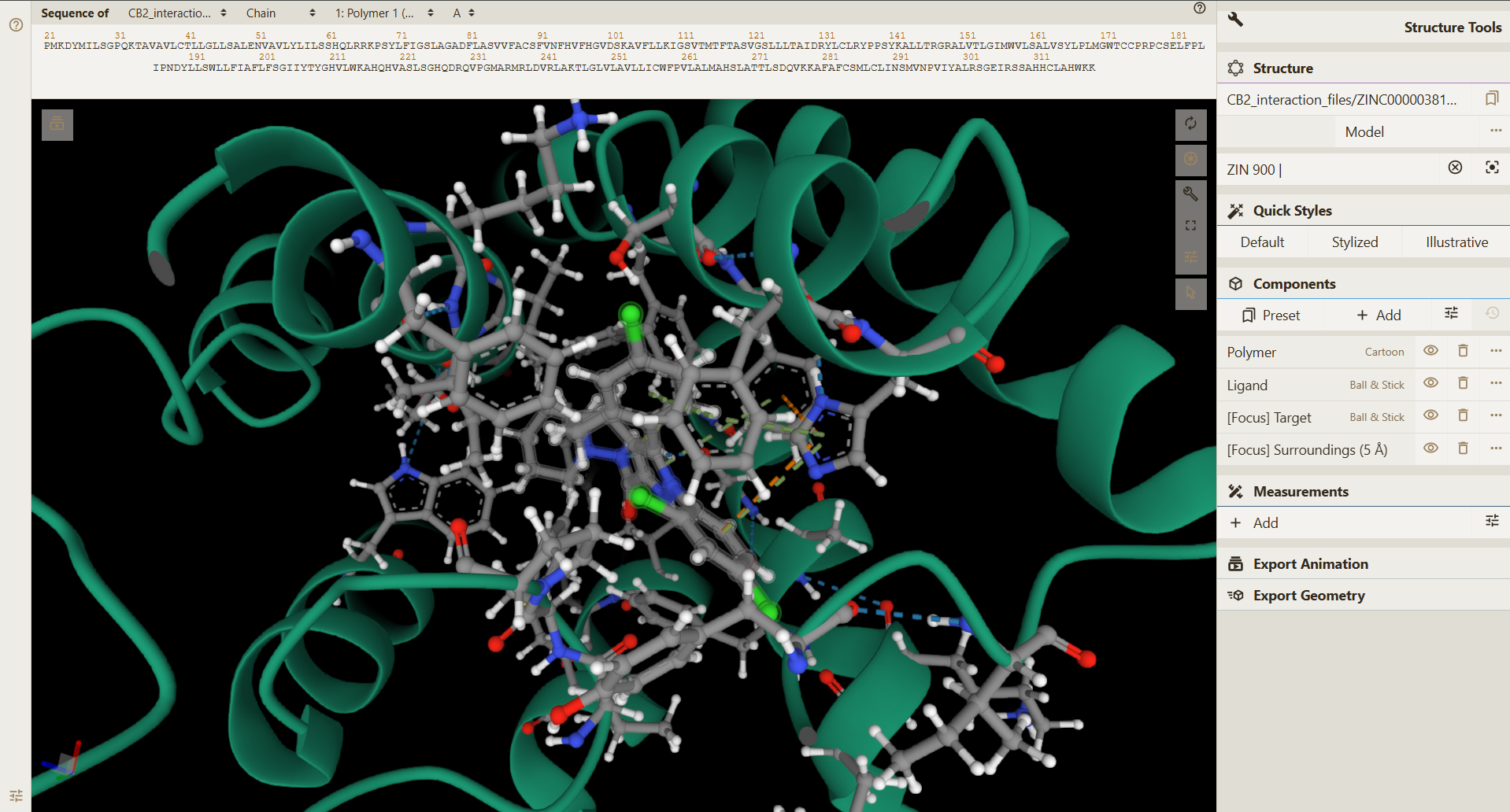
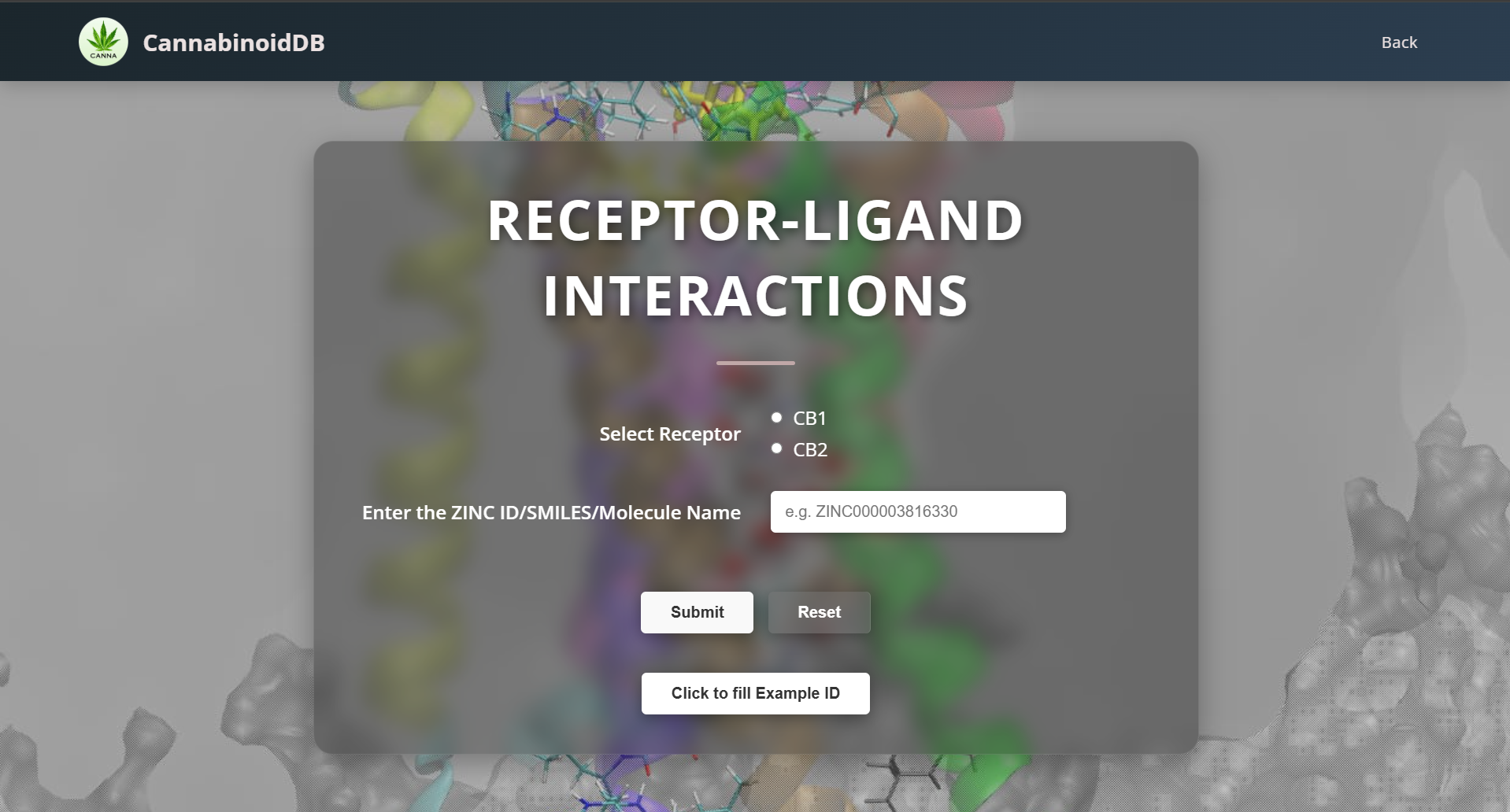
Interactions
The receptor and ligand molecules have been docked using the Glide* module of Maestro interface in Schrodinger software. To look into the interactions of that particular molecule with the chosen receptor, click on View option under Interactions column for that particular molecule OR You can directly access the Interactions Tool in the Functions section of the Homepage.
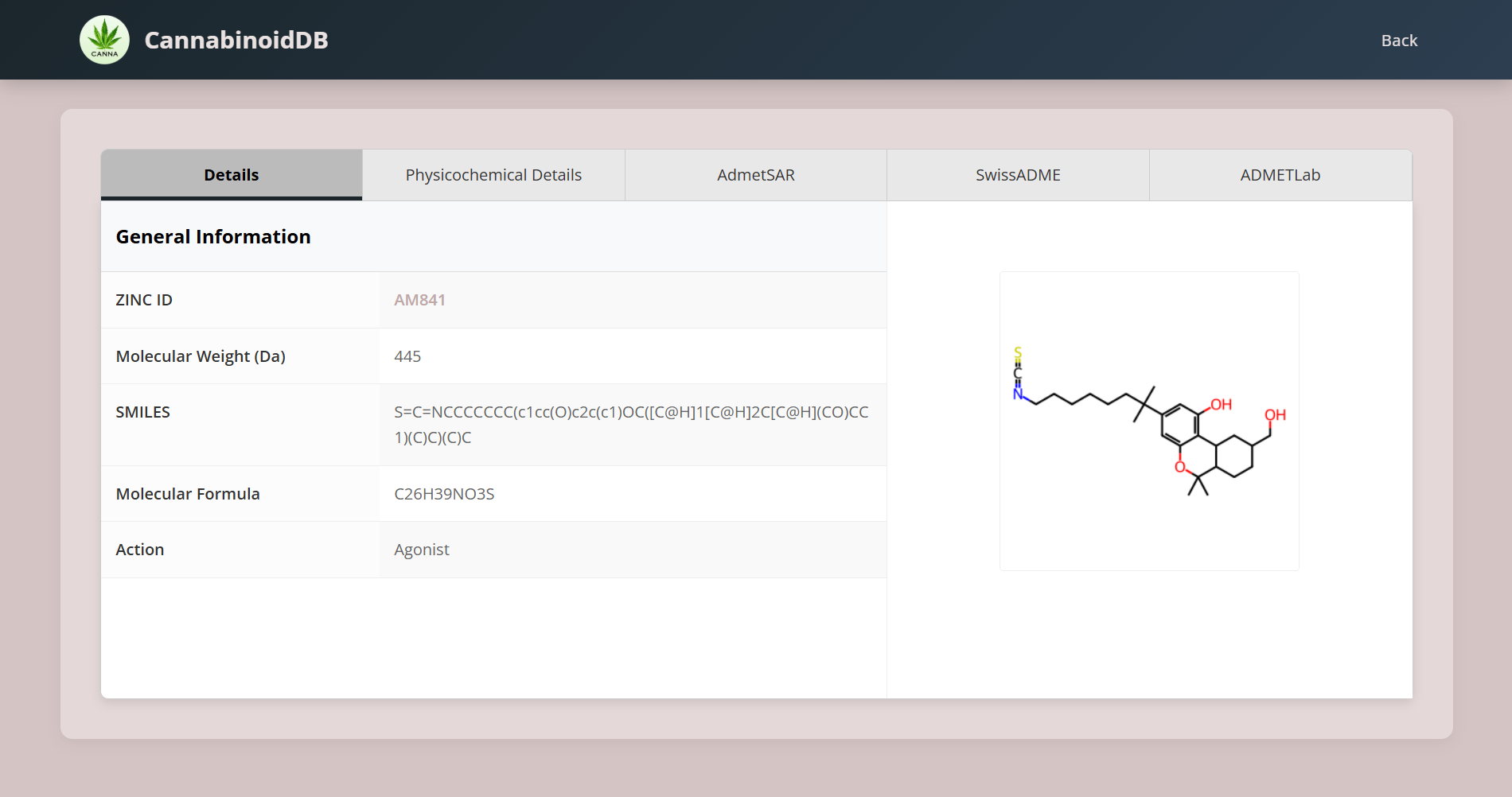
Molecules Details
To look into the general properties, physiochemical and pharmacokinetic properties, ADMETLab*, ADMETSAR* and SwissADME* properties of the respective molecule, click on View option under Details column.
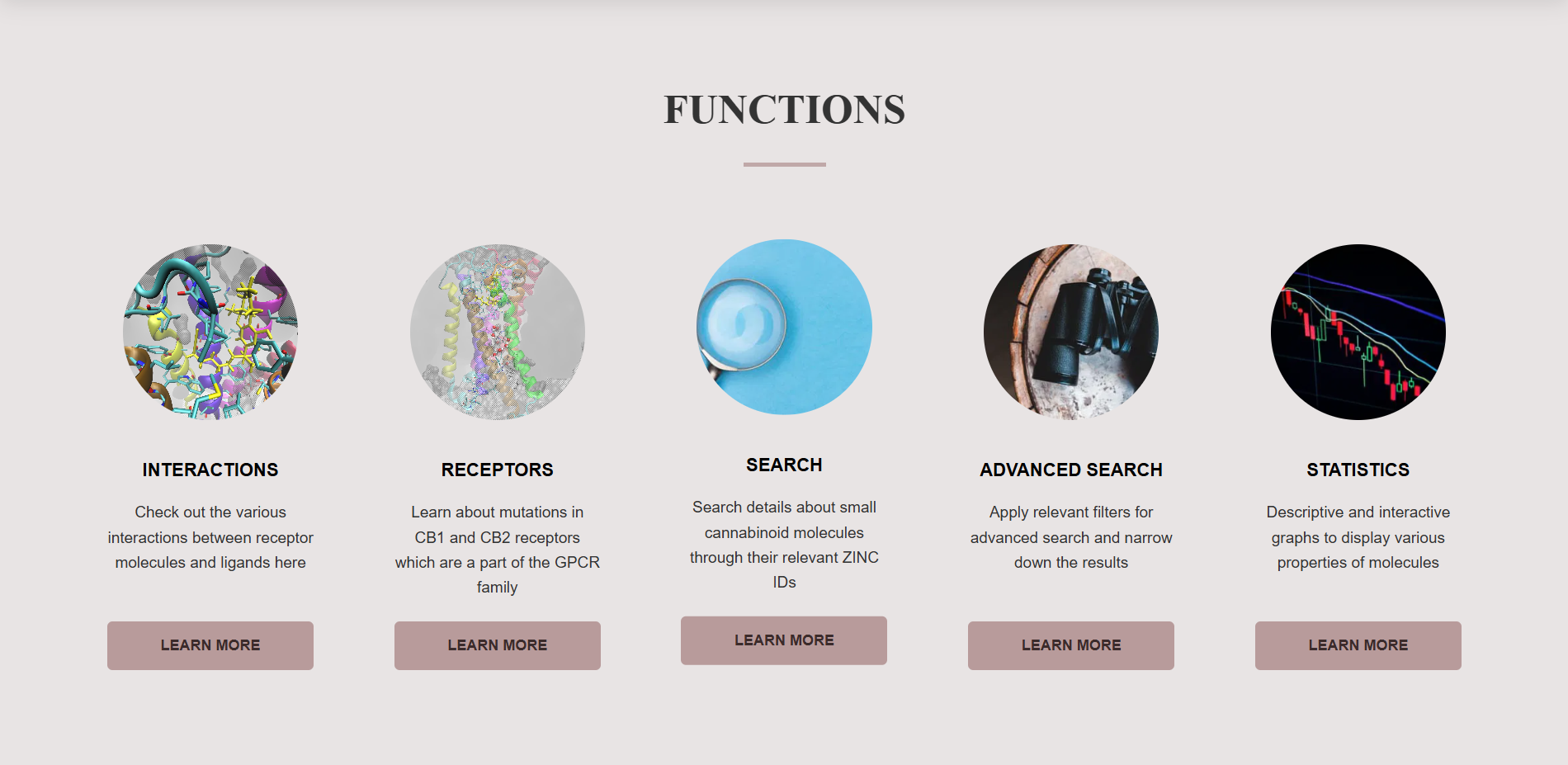
Functions and Tools
The receptor and ligand molecules have been docked using the Glide* module of Maestro interface in Schrodinger software. To view the interactions of a particular molecule with the chosen receptor, click on Learn More button of Interactions Tool in Functions section.
Mol* Plugin
Choose your required ligand molecule's ZINC ID/SMILES from the database and the respective receptor. The interactions are displayed in a standard PDBe Molstar (Mol*) Plugin window.
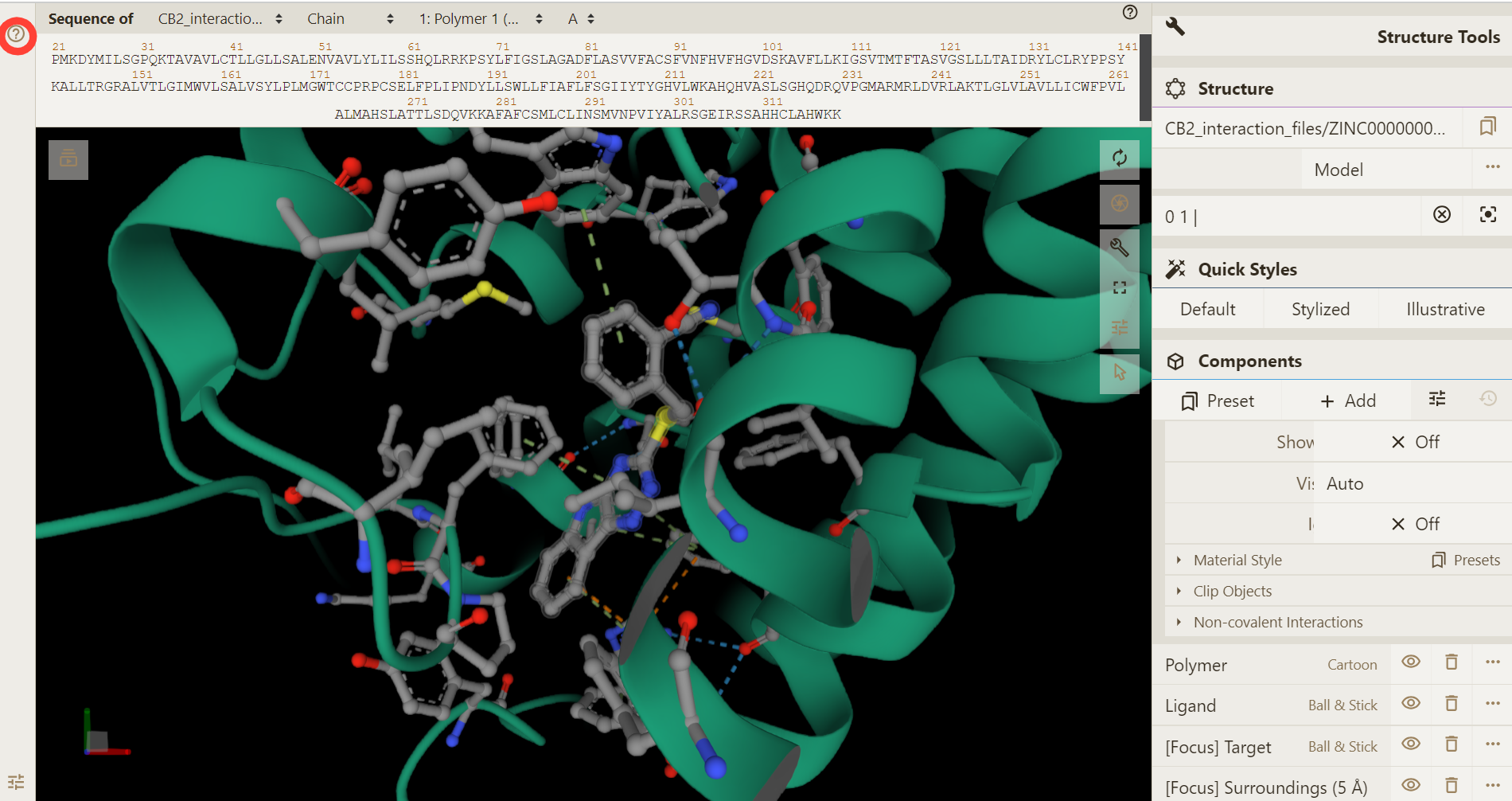
If you encounter any problem during the visualization, click on the "?" button on the left side of plugin window for help.
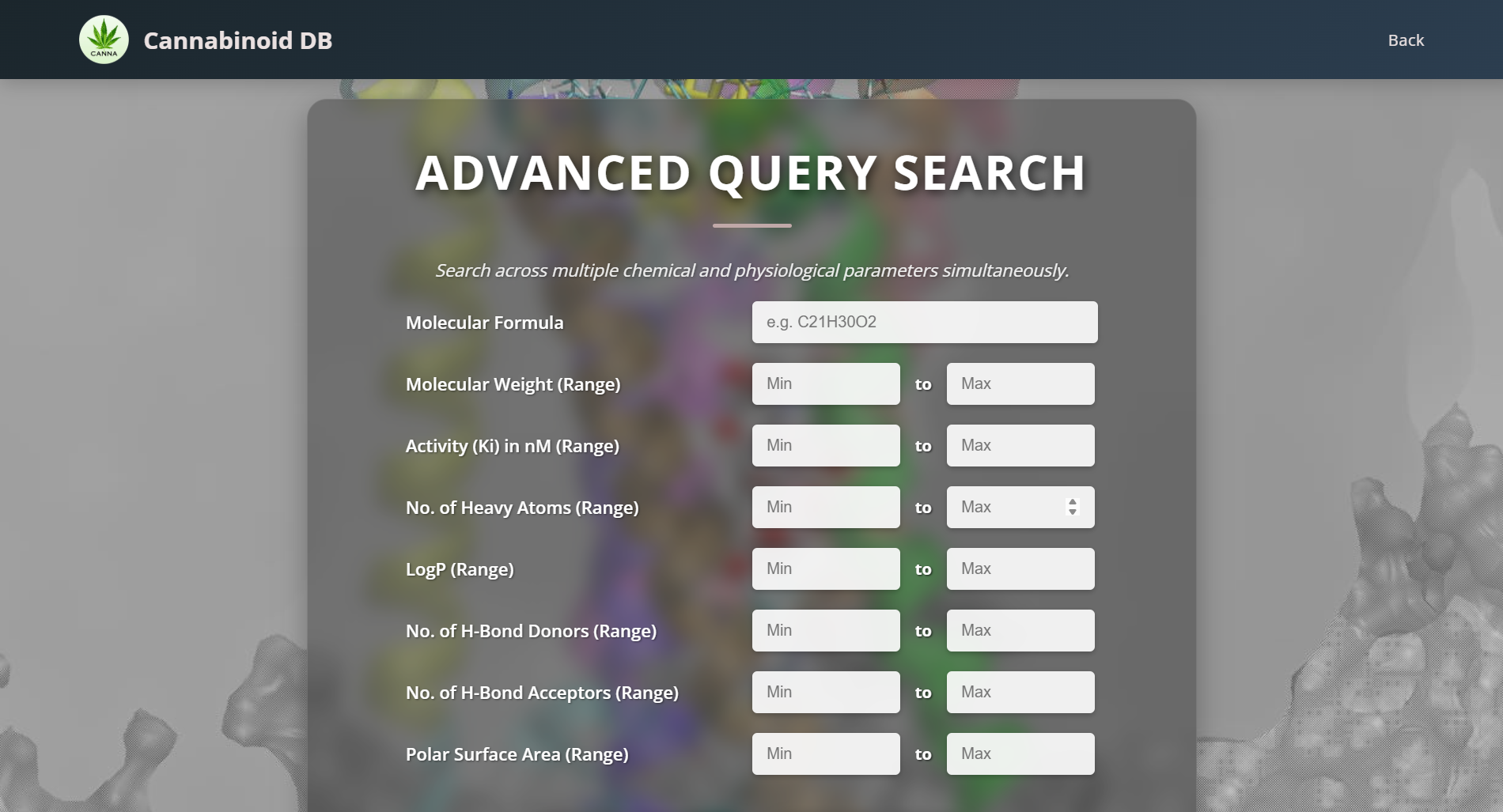
Advanced Search Tool
Use this tool to narrow down and refine your search results. Enter property ranges for Molecular Formula, Molecular Weight, Number of Heavy Atoms, and AlogP values.
References and Citations
- Glide:
- Yang, Y; Yao, K; Repasky, M.P.; Leswing, K; Abel, R; Shoichet, B.K.; Jerome, S.V., Efficient Exploration of Chemical Space with Docking and Deep Learning. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 11, 7106–7119
- Friesner, R. A.; Murphy, R. B.; Repasky, M. P.; Frye, L. L.; Greenwood, J. R.; Halgren,T. A.; Sanschagrin, P. C.; Mainz, D. T., J. Med. Chem., 2006, 49, 6177–6196
- ADMETLab:
- Dong, J., Wang, NN., Yao, ZJ. et al. ADMETlab: a platform for systematic ADMET evaluation based on a comprehensively collected ADMET database. J Cheminform 10, 29 (2018).
- ADMETSAR:
- Hongbin Yang, Chaofeng Lou, Lixia Sun, Jie Li, Yingchun Cai, Zhuang Wang, Weihua Li, Guixia Liu, Yun Tang. admetSAR 2.0: web-service for prediction and optimization of chemical ADMET properties. Bioinformatics, 2018, bty707.
- SwissADME:
- A. Daina, O. Michielin, V. Zoete. SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017; 7:42717.
- ZINC:
- Irwin, Tang, Young, Dandarchuluun, Wong, Khurelbaatar, Moroz, Mayfield, Sayle, J. Chem. Inf. Model 2020